3-2-1 Backup Rule: The Three Steps in Developing a Backup Strategy
3-2-1 backup strategy involves creating three copies of your data, storing them on two different types of media, with one copy kept offsite for added security. Handy Backup is the perfect tool for implementing this efficient technique, recognized as one of the most efficient strategies.
Take control of your data security today! Download the free trial version of Handy Backup and experience the peace of mind that comes with a robust backup strategy.
What is 3-2-1 backup rule (strategy)?
The 3-2-1 backup strategy is widely recognized as one of the most effective methods for creating data backups.
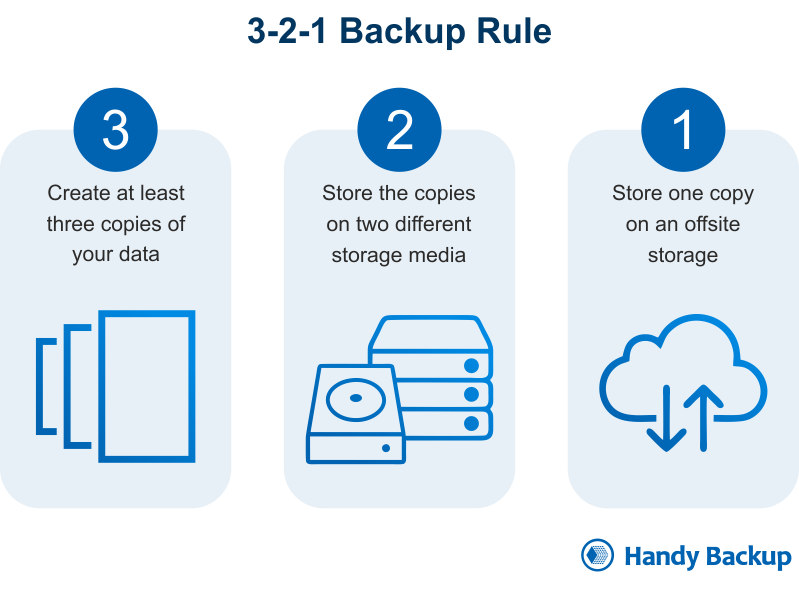
The principles of the 3-2-1 backup rule are straightforward and universally applicable:
- Generate a minimum of 3 copies of data, stored on physically distinct storage media;
- Maintain these copies in no fewer than 2 different formats;
- Always store at least 1 of these backups off-site (e.g., on a commercial cloud account).
Strictly adhering to these simple guidelines as part of a "3-2-1 backup plan" can be a lifesaver for system administrators and experienced PC users in various scenarios.
Explanation of Terms
To provide a deeper understanding of the 3-2-1 backup strategy, let's delve into the terminology associated with this approach.
The Three Copies
Creating three or more copies of data on different storage devices mitigates risks inherent to specific devices. For example, hardware failure may affect a hard disk but not a cloud account; network mishaps might interrupt online data transfer but won't impact copying from a local disk, and so forth.
The Two Formats
The term "format" refers to physically different representations of data, not just logical layouts. If one copy is stored as hard disk data, ensure at least one other copy is on FTP, tape, or a cloud service. This safeguards data from storage-specific risks.
The One Offsite Copy
The final principle of the 3-2-1 backup rule emphasizes keeping one or more backups off-site, i.e., not in the same room/building as the original. This ensures that if the original and local copies are physically destroyed (due to theft, fire, war, earthquake, or any other force), at least one data copy will be preserved.
Note: Nowadays, the optimal choice for offsite storage is often a commercial cloud. Options like Amazon S3, popular services like Dropbox or Google Drive, or even utilizing an FTP server are viable solutions for implementing the 3-2-1 backup strategy.
Version 8.5.3 , built on March 5, 2024. 116 MB
30-day full-featured trial period
By adopting this server backup strategy, you can ensure the security of your data. To implement the 3-2-1 rule for backup right away, all you need to do is download Handy Backup.
Technical Requirements for 3-2-1 Rule
The implementation of the 3-2-1 backup rule requires the availability of suitable storage devices, accounts, or vaults. However, there are specific requirements for these storage devices:
- Stable network connections are essential for online storage.
- Each storage type must have sufficient free space to accommodate regular backups.
- Both the physical and logical availability of each storage device are crucial during scheduled backup operations.
The significance of the last requirement can be clarified using the example of employing a USB drive for the 3-2-1 backup strategy. Clearly, this drive must be connected to a PC during scheduled backups. If this connection could interfere with other tasks, a viable alternative is to use a local drive instead.
Use Cases for 3-2-1 as Data Backup Strategy
The 3-2-1 rule is versatile and applicable to a wide range of use cases, making it a preferred choice compared to more complex methods like Grandfather-Father-Son or Tower of Hanoi backup strategy. It can be effectively employed for various types of data backup, including:
- Back up photos, pictures, images, movies, audio files, and other multimedia content;
- Saving projects and work files, either for safekeeping or for sharing/co-working;
- Securing database copies, back up websites, CMS content, and saving online shops, etc.;
- Creating backups of crucial databases or arrays of virtual machines*.
While the 3-2-1 backup strategy is well-suited for various backup scenarios, it may not be the optimal choice for creating disk images. However, this is not a strict rule, and the 3-2-1 data backup strategy can still be used for system recovery if needed. It's a versatile approach that offers redundancy without strict limitations!
* Databases and virtual machines are supported in Handy Backup Small Business and Handy Backup Server Network.
Opportunities and Challenges in Modern Day
Recent advancements in data protection have expanded the scope of data applications, including tasks like populating data repositories and conducting extensive analyses on large datasets. This extends beyond traditional insurance practices, as companies engage in testing and perform analytical assessments.
However, challenges emerge with evolving regulations such as GDPR, introducing complexity by mandating strict security measures and the ability to delete specific user data from all backup copies. Deleting data can be a daunting task, especially when distributed across different systems and storage locations. It's crucial to acknowledge that compliance with such requirements may face hindrances due to technical limitations or legal obligations. Despite these complexities, the 3-2-1 backup approach remains pertinent. Additional steps, such as recovery testing and granular data searches, have become integral components of modern data protection strategies.