Physical Data Backup
Physical backup means creating a complete copy of actual files and storage structures — such as whole disks, partitions, or system folders — by accessing them at the file system or device level using standard file system queries, rather than through application-level interfaces. Unlike a logical backup, which works via export tools, physical data backup captures raw binary data exactly as it exists on disk, including system files, boot records, and hidden data.
Version 8.6.8 , built on Fabruary 13, 2026. 152 MB
30-day full-featured trial period
Try our powerful Handy Backup with a free 30-day trial and experience robust, full-scale physical backup and recovery that protects your entire system, not just selected files. Discover how easy it is to create disk images or back up critical volumes — with full recovery just a few clicks away.
Physical Backup vs Logical Backup
Understanding the key distinctions between these two backup approaches helps you choose the right strategy for protecting your data. Each method works differently, offering unique advantages and trade-offs depending on your system’s needs and recovery goals.
What is backed up?
Logical backup captures data through the application interface, targeting specific tables, queries, or exports in SQL format. The physical data backup works at the file system level, copying complete database files or full disk images for a more comprehensive snapshot.
Is system downtime required?
Data extraction through the application can occur without interrupting system operations, allowing backups “on the fly.” In contrast, full file-level copies generally require pausing or freezing activity to maintain data integrity during the process.
Recovery flexibility
This logical approach enables restoring individual tables or records selectively, providing precise control over the recovery process. The physical backup method restores the entire dataset or system configuration, offering a complete recovery solution but less granularity.
Speed and data volume
Copying raw files directly makes the file-level backup significantly faster, especially for large data volumes. Conversely, extracting data through application queries generally takes longer due to additional processing overhead and complexity.
Advantages of Handy Backup's Physical Backup Software
Sector-Level Disk Copying
Handy Backup creates disk images by copying data at the sector level, preserving exact physical structure, including unused space and system metadata.
Backup of Bootable Partitions
Physical backup includes bootloaders and system partitions, making it possible to fully restore or clone bootable systems without reinstallation.
Snapshot-Based Backup with VSS
Using Volume Shadow Copy Service, the software captures the physical state of the disk at a single point in time, even if the system is running.
Strong Encryption for Data Security
All physical backup data can be encrypted using industry-standard algorithms, protecting your sensitive information from unauthorized access .
Hidden and System Area Coverage
All hidden sectors, recovery partitions, and system-reserved areas are included in physical backups, ensuring nothing is missed during recovery.
Exact Environment Replication
You can replicate a system’s full disk environment to another machine or disk, preserving drivers, configurations, and special system files.
Automated Backup Scheduling
Schedule physical computer backup to run automatically at convenient times, ensuring your data is protected regularly without manual intervention.
Full Restore Without Dependencies
Physical backups can be restored without requiring the original application, operating system, or environment to be present or functional.
How to Take a Physical Backup with Handy Backup
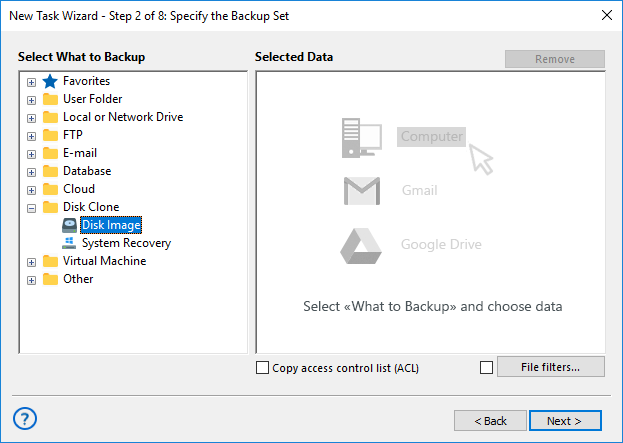
- After selecting "Backup" as the task type, navigate to the "Disk Clone" group and select the "Disk Image" plugin to back up a specific disk partition.
- Next, specify the exact disk partition you want to back up by browsing through the available drives and selecting the desired partition.
Note: Entire computer backup is recommended when you need full disaster recovery or plan to migrate your system to a new machine, while partition backup is more suitable for duplicating specific drives, testing configurations, or preserving certain environments independently.
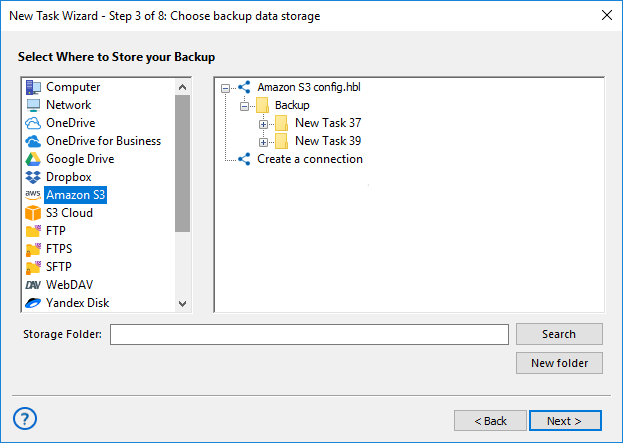
- Now, choose the destination where your physical backup will be stored. This can be a local drive, an external hard disk, a network share, or a cloud storage service integrated with Handy Backup.
- Configure additional options such as encryption settings to protect your backup data and set up automatic scheduling to run backups regularly without manual intervention.
- Finally, name your backup task for easy identification, review all settings, and confirm to start the backup process for different types of physical servers, and more.

Note: For enterprise and infrastructure-level protection, Handy Backup also offers a dedicated solution for physical server environments. Our physical server backup software is designed to safeguard Windows and Linux servers, databases, virtual machines, and network resources from a single centralized console. It ensures reliable disaster recovery, automated scheduling, and secure data handling across complex server infrastructures.
Physical Backup Limitations
No Item-Level Restore
Physical backup cannot restore individual records or files. For selective recovery, logical backup is more suitable.
Risk in Running Apps
Active apps may store unsaved data in memory. Without VSS or app tools, backups can be inconsistent.
Large Size and Time
Disk-level backups use more space and restore slower, especially if only partial data needs to be recovered.
Hardware Dependency
Restoring to different hardware may cause driver or boot issues. Hardware compatibility must be checked.
Frequently Asked Questions About Physical Backup Tools
- What is an example of a physical backup in real-world scenarios?
A common example of a physical backup is creating a full disk image backup of your system drive. This type of backup captures all data sectors on the disk, including the operating system, installed applications, configuration files, and hidden system areas. It’s often used for disaster recovery, hardware migration, or cloning work environments. Handy Backup supports physical backups through its Disk Image functionality, allowing you to create sector-level copies of hard drives, partitions, and bootable systems. You can schedule regular backups, encrypt data, and restore the entire environment in a few clicks.
- How to take a physical backup in MySQL?
To perform a MySQL physical backup, you typically copy the database’s data directory, which contains all the binary files for tables, indexes, and logs. This process requires the database to be stopped or locked to avoid inconsistencies. Alternatively, tools like `mysqlbackup` or filesystem-level snapshots using LVM or VSS can be used. Handy Backup simplifies this process by allowing you to back up the MySQL data directory as part of a full system or disk-level backup. It integrates with Volume Shadow Copy to ensure consistency and can run backups automatically, even while MySQL is active.
For a comprehensive overview of best practices and methods, check out our db backup strategy guide.
- What is one of the major benefits of physical backups over logical backups?
One major benefit of physical backups is the ability to capture an exact, sector-by-sector copy of the entire storage device or partition. This ensures that every bit of data, including system files, application data, and metadata, is preserved perfectly, enabling faster system recovery. Physical backups also reduce the risk of data loss due to incomplete or inconsistent exports that can occur with logical backups. Handy Backup excels in creating reliable physical backups using its Disk Image plugin, which allows users to create precise images of hard drives and partitions, supports incremental updates to save storage space, and integrates encryption and scheduling.
Learn more:
- InnoDB Storage Engine: Benefits, Usage, and Optimization
"Many users wonder what is InnoDB in MySQL? InnoDB is a powerful and widely-used storage engine for MySQL databases, designed to deliver reliability, performance,…" - MySQL Master Server
"MySQL Slave Server is a server configured for MySQL replication. It constantly monitors and replicates all changes made to the database on the Master Server.…" - MySQL Login Scripts
"MySQL login scripts play a crucial role in facilitating secure and efficient access to database repositories. There are many platforms that utilize MySQL…"