Logical Backup in Databases
Logical backup means creating a reliable copy of data used by an application — like database tables — by accessing them directly through the app’s own interfaces. Unlike a physical backup, which simply copies files on the system, logical backup is more accurate because it captures data that might still be in memory and hasn’t yet been saved to disk.
Try our powerful Handy Backup with a free 30-day trial and experience reliable, precise logical backup software that protect your critical data effortlessly. Learn how to take a logical backup with ease and keep your data safe and easily restorable — no risk, no commitment.
Version 8.6.8 , built on Fabruary 13, 2026. 152 MB
30-day full-featured trial period
Advantages of Logical Backup
Logical database backup offers several key benefits that make it an ideal choice for protecting your important data.
High Accuracy
Logical backup accesses data via the application’s interfaces, capturing both saved data and data still in memory for a complete, consistent copy.
Non-Disruptive Backups
Logical backups can be performed while the system is running without interrupting normal operations. This allows continuous access to your data during the backup process.
Simplified Restoration
Backups are stored in a structured, readable format, making it easier to restore individual tables or records. This flexibility speeds up recovery and reduces the risk of errors.
Difference Between Logical Backup and Physical Backup
When planning a database backup strategy, it’s important to understand the difference between physical backup and logical backup. These two approaches serve different purposes and are suited to different scenarios. The table below highlights the key distinctions to help you choose the right method for your database backup needs.
| LOGICAL BACKUP | PHYSICAL BACKUP | |
|---|---|---|
| Backup level | Data via the application’s interface | Files at the operating system level |
| Data accuracy | High — includes in-memory data | Depends on file state at time of copy |
| Can run while system is active | Yes — no need to stop the application | Often requires downtime or locking |
| Restore flexibility | Restore individual tables or records | Restores the entire system or data set |
| Version compatibility | High — stored in portable format | Low — tied to specific versions or structure |
| Speed | Slower — depends on data volume | Faster — copies raw files or disk blocks |
| Storage format | Structured (e.g., SQL script or export file) | Binary files or disk images |
| If you want flexibility, the ability to back up while your systems are running, and easy restoration of specific data like individual tables — logical backup is the better choice. | If you need faster, more comprehensive system-level backups and can afford some planned downtime, a physical backup may be more suitable. |
Note: For many businesses, the best strategy is to combine both types — using logical backup for day-to-day data protection and physical backup for full system recovery. Learn more about different types of physical servers to ensure secure and reliable backup solutions.
Advantages of Handy Backup's Logical Backup Software
Support for Various Databases
Handy Backup supports a wide range of databases, including logical backup in MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and more, ensuring seamless protection of structured data across multiple platforms.
AES-256 Encryption for Security
You can store backups on various destinations such as local disks, network drives, FTP servers, or cloud services like Amazon S3, offering maximum flexibility and scalability for your storage needs.
Automated Scheduled Backups
Handy Backup allows you to automate your backups by setting custom schedules, ensuring your critical data is backed up regularly without manual intervention or missed cycles.
Incremental Backup Capabilities
Logical backups support incremental mode, which saves only changes made since the last backup. This optimizes backup speed and reduces storage consumption while keeping data current.
Remote Backup via Web Application
Manage and execute backups remotely using Handy Backup’s web app, provided the software is running on a Windows machine. This enables offsite control and monitoring of your backup jobs.
Native, Structured Backup Format
Logical backups are saved in native formats like SQL scripts or export files, which makes restoring individual tables or records fast, flexible, efficient, and less error-prone.
User-Friendly Interface
With a clean and intuitive interface, setting up backups is straightforward, even for non-technical users. Our logical backup tools guide you step-by-step through the process.
Multiple Backup Destinations
You can store your backups on various destinations such as local disks, network drives, FTP servers, or cloud services like Amazon S3, offering maximum flexibility and scalability for your storage needs.
How to Perform PostgreSQL Logical Backup to Amazon S3 with Handy Backup
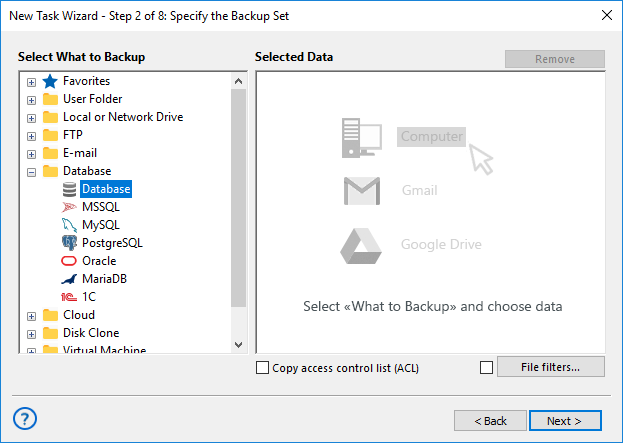
- Launch the New Task Wizard, select a backup task, then choose PostgreSQL from the Database group on Step 2.
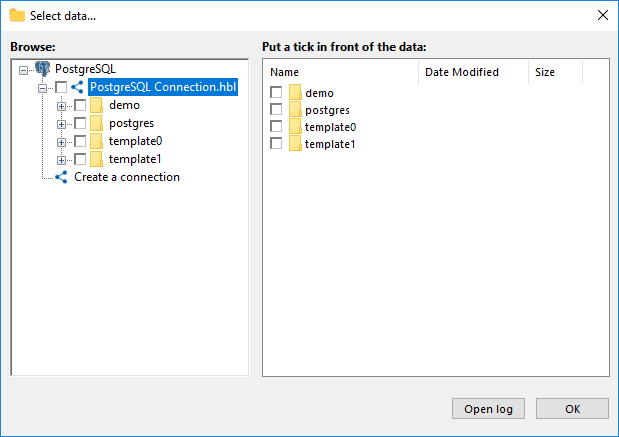
- If you haven’t done so, create a new connection and fill in your database credentials (host, port, username, etc.).
- Select the specific PostgreSQL tables or entire schema you wish to back up.
Note: For efficient PostgreSQL backup, make sure your DB user has sufficient privileges to run SELECT queries on the desired tables or schema.
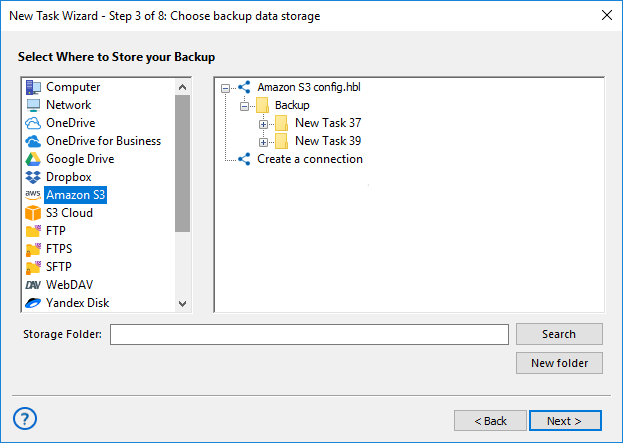
- Proceed to Step 3 and choose Amazon S3 as the destination for your backup data.
- On Step 4, optionally enable compression, encryption, and set versioning or retention policies.
- Configure a schedule to automate the backup task (e.g., daily or weekly), then save and finish.
Tip: For PostgreSQL, differential backups are recommended over incremental, as they offer better performance and consistency with logical data structures.
Frequently Asked Questions About Logical Backup Tools
- What is a Logical Backup?
A logical backup involves exporting database objects such as tables, schemas, or records into a format that can be easily read and restored, such as SQL scripts or export files. Unlike physical backups, which copy raw database files, logical backups provide flexibility by allowing selective restoration of individual elements. Handy Backup supports logical backups by enabling scheduled exports of database data in native formats, ensuring secure storage and easy restoration on demand.
- What is the Difference Between Logical Backup and Physical Backup?
Logical backups capture the database content by exporting data and database objects into a portable format, enabling flexible restoration of specific parts of the database. Physical backups, on the other hand, involve copying the actual database files at the storage level, which is faster but less flexible. Handy Backup expertly supports both backup types with robust encryption and flexible scheduling, making it the trusted choice for businesses seeking reliable and secure data protection.
- How to take logical backup in Oracle?
Taking a logical backup in Oracle typically involves exporting database schemas or tables using tools like Oracle Data Pump or exp/imp utilities, which create export files containing SQL statements. Handy Backup simplifies this process by integrating Oracle backup plugins that automate export tasks, allowing users to schedule logical backups with encryption and store them securely in locations such as Amazon S3. This approach reduces manual effort and ensures consistent, reliable backups.
Learn more:
- Foreign Key
"Foreign key is a field in a “child” table of a database that is used to refer to a record in a “parent” table of the same database. For example, if there…" - Oracle VSS Writer Service
"VSS Writer Service is an addition to Windows Volume Shadow Copying Service (VSS) provided by an Oracle API, to allow access to open Oracle databases. Having…" - What is Database Architecture - Definitions and Terms
"Database architecture is the high-level design that defines how data is organized, stored, processed, accessed, and secured across a system. It outlines…"